ネットワーク監視ソフトNagios3をインストール
ブログにも書いたが、ホームページを公開して以来我が家の光回線であるSTnetのPikaraから割り振られているIPアドレスがちょくちょく変化し、結果としてダイナミックDNSとの連係が一時的に切れる現象が出ている。
これではアクセスしようという気にならないのではと思い、一度どの位切れているかを定量的に把握したく、かってメルコのリンクステーションをハックして作っていたサーバーで運用していたNagiosを使ってみることとした。
Nagiosは定期的(デフォルト5分間隔)にpingを打ってくれてダイナミックDNSが上手く稼働しているかどうかを検知し、また統計的な集約も出来るのでうってつけである。
かって実施したインストールはソースからコンパイルしたが、今回は他のアプリケーションと同じでapt-get install でインストール出来るので簡単である。Nagiosには他に監視状況を表示させるためにApach2が必要となるが、既にインストールされている場合はNagios3だけでOKである。
sudo apt-get install nagios3
sudo apt-get install apache2
nagios3はインストール途中でnagiosadminのパスワードを聞いてくるので適当に入力する。これは/etc/nagios3/htpasswd.usersに保存される。
インストール後は各アプリケーションの設定を行う。
その前に監視の仕組みは
Nagiosは各ホストとhttpdなどのサービスのステータスを収集し、Apacheでそれを表示するというのが監視の流れにである。
Nagiosの設定ファイル等については
/etc/nagios3
以下にある。
このうち主となるconfigファイルは
/etc/nagios3/nagios.cfg
で、ここから他のconfigをファイル指定またはフォルダ指定で追加している構造となっている。
フォルダで指定した場合、読み込むのは末尾.cfgのファイルなので新規に作成したconfigファイルを読み込ませる際には忘れぬよう注意が必要である。
Nagiosをインストールした段階でNagiosサーバ自身=localhostへの監視は自動で始まってる。
それに使用されているconfigファイルは
/etc/nagios3/conf.d/localhost_nagios2.cfg である。
〇Nagios3
Nagiosの監視は対象ホストとそのホストで実施しているサービスである。
監視したいホストとサービスを拡張子をcfgとしたファイルで指定する。
デフォルトのnagios3が動いているホストの監視指定は以下の通りである。つまり、/etc/nagios3/conf.d/以下に拡張子cfgのファイルを置けば監視してくれる。
pi@wp-test:~ $ cat /etc/nagios3/conf.d/localhost_nagios2.cfg
# A simple configuration file for monitoring the local host
# This can serve as an example for configuring other servers;
# Custom services specific to this host are added here, but services
# defined in nagios2-common_services.cfg may also apply.
#
ホスト登録
define host{
use generic-host ; Name of host template to use
host_name localhost
alias localhost
address 127.0.0.1
}
# Define a service to check the disk space of the root partition
# on the local machine. Warning if < 20% free, critical if
# < 10% free space on partition.
ホストに関するサービスの監視を登録
define service{
use generic-service ; Name of service template to use
host_name localhost
service_description Disk Space
check_command check_all_disks!20%!10%
}
# Define a service to check the number of currently logged in
# users on the local machine. Warning if > 20 users, critical
# if > 50 users.
define service{
use generic-service ; Name of service template to use
host_name localhost
service_description Current Users
check_command check_users!20!50
parents localhost ⇒ 上位hostを指定
}
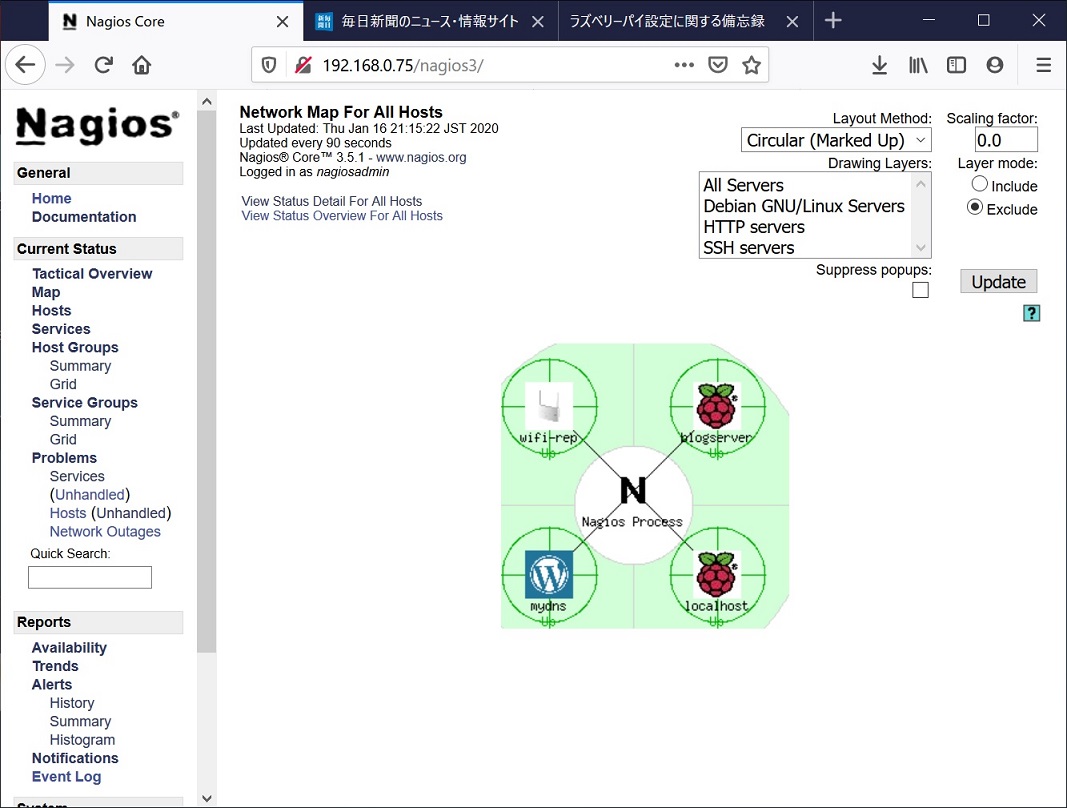
次に、statusmapで表示するアイコンを/etc/nagios3/conf.d/extinfo_nagios2.cfgで登録する。
ホスト表示に使うアイコンはサイズ40x40のgif,jpg,pngとユーティリティを使って作成するgd2タイプの画像を/usr/share/nagios3/htdocs/images/logos/以下に配置する。指定方法は以下の通りであり、設定した全てのホストに対応して指定しないとエラーとなる。
ここでGD2画像の作成方法は
$ sudo aptitude install libgd-tools でツールをインストールし、
$ pngtogd2 image.png image.gd2 1 1 で変換する。
アイコンの登録は以下の通り、/etc/nagios3//extinfo_nagios2.cfgで行う。
pi@wp-test:~ $ cat /etc/nagios3/conf.d/extinfo_nagios2.cfg
##
## Extended Host and Service Information
##
define hostextinfo{
hostgroup_name debian-servers
notes Debian GNU/Linux servers
# notes_url http://webserver.localhost.localdomain/hostinfo.pl?host=netware1
icon_image debian.png
icon_image_alt Debian GNU/Linux
vrml_image debian.png
statusmap_image debian.gd2
## 2d_coords 200,200
}
define hostextinfo{
host_name blogserver
notes BlogServer
icon_image raspi.png
icon_image_alt Raspi
vrml_image raspi.png
statusmap_image raspi.gd2
## 2d_coords 450,50
}
〇apache2
/etc/apache2/apache2.confの最後に以下の内容を追記する。
Alias /nagios3/stylesheets /etc/nagios3/stylesheets
Alias /nagios3 /usr/share/nagios3/htdocs
Options FollowSymLinks
DirectoryIndex index.php index.html
AllowOverride AuthConfig
Order Allow,Deny
Allow From All
AuthName "Nagios Access"
AuthType Basic
AuthUserFile /etc/nagios3/htpasswd.users
require valid-user
Options +ExecCGI
これでapache2とnagios3を再起動すると監視が始まる。
以下はステータスマップの様子。